|
|
 |
PyScatman
The PyScatman module is a tool to perform a wide-angle coherent diffraction simulation, based on the Multi-Slice Fourier Transform (MSFT) approach.

Jolab
Jolab is a free and open-source Julia package to simulate light propagation in optical systems. The package implements rigorous, full-wave optical models to simulate light propagation on setups. The package is built to be easily usable by any user independent of its background in theoretical optics.

PyFocus
PyFocus is a Python package that provides high-level functions and an user interface to perform full vectorial calculations of the focus of an electromagnetic field that has been modulated by a custom phase mask.

Gaussian beam without approximation
We use the angular spectrum representation to compute exactly the Gaussian beam close to the waist (w0) in the case of highly nonparaxial field (w0<λ). The computation is done in the vectorial case for a polarized Gaussian beam. In the area of the waist, the contribution of the propagating and evanescent waves is discussed. Moreover, the Gaussian wave is developed in terms of series, which permits to get analytical expressions for both propagating and evanescent waves when the observation is close to the waist.
PyTMM
Transfer Matrix Method implementation & RefractiveIndex.info database (2015-05-24) browser for layered systems of isotropic dielectric materials.
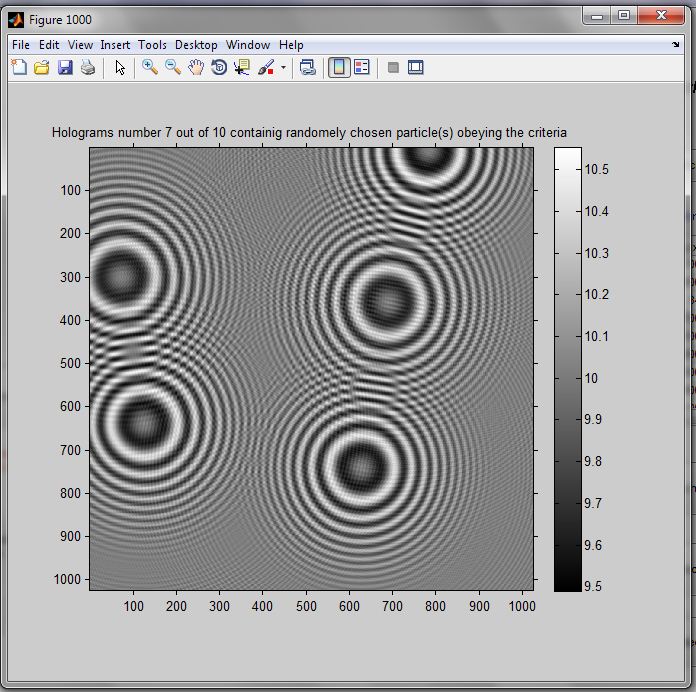
HoloRec3D: Digital Holography Matlab Toolbox
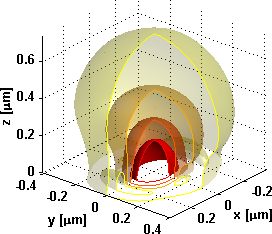
Focus field calculations
In analogy to the classical Debye formulation and the seminal work by Wolf and Richards, This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. reformulated the calculation of the electromagnetic field in the focus of high numerical aperture objectives based on a Fourier or chirp z transform.
layerlab: A Python-based toolbox for computations involving layered materials.
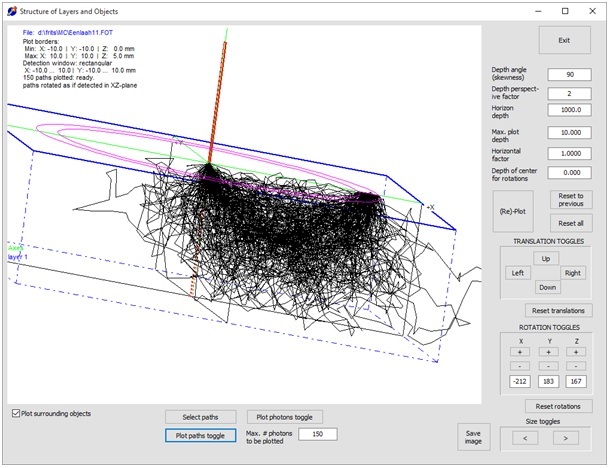
MontCarl, Monte-Carlo simulations of light scattering and absorption in turbid media, like tissue.
|
|
 |
|

