|
|
 |
A software called PyMultiLab which can calculate the electromagnetic properties of multilayered spherical particles.
Online nearfield Mie calculator

MATLAB interface to Warren Wiscombe's MIEV0 Fortran77 code such that it is possible to easily use MIEV0 by directly calling it from MATLAB.
[Qext, Qsca, Gqsc, S1, S2, Sforw, Sback, Tforw, Tback, Spike, PMOM] = ...
mlMIEV0(XX, Crefin, Perfct, Mimcut, Anyang, Numang, Xmu, Nmom, Ipolzn, Momdim, Prnt, Verbose);
LX-MIE is a Mie scattering code that calculates:
- Mie efficiencies, cross sections, and asymmetry parameters
- Scattering phase functions for a given set of scattering angles
- Representation of the phase function as a Legendre series
James Lock's Fortran code for the Finely stratified sphere model (Vol. 25, No. 12/December 2008/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A).
- Link (28 Aug 2025) local copy
x
x
NeuralMie, a neural network Mie scattering emulator that can directly compute the bulk optical properties of a diverse range of aerosol populations and is appropriate for use in atmosphere simulations where aerosol optical properties are parameterized.
A complete Fortran Mie Scattering program for homogeneous and non-homogeneous spherical particles.
 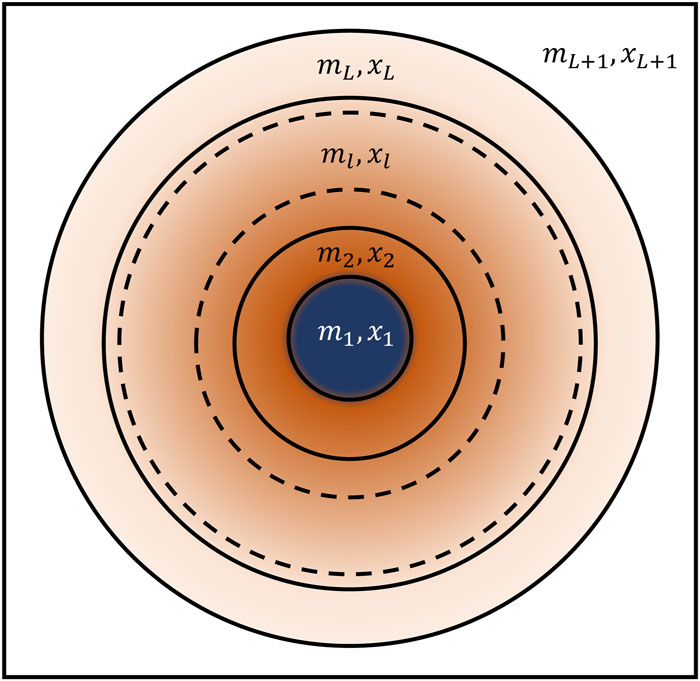
This Julia package provides semi-analytical solutions to the scattering of time harmonic and static electromagnetic fields from spherical objects (amongst others known as Mie solutions or Mie scattering).

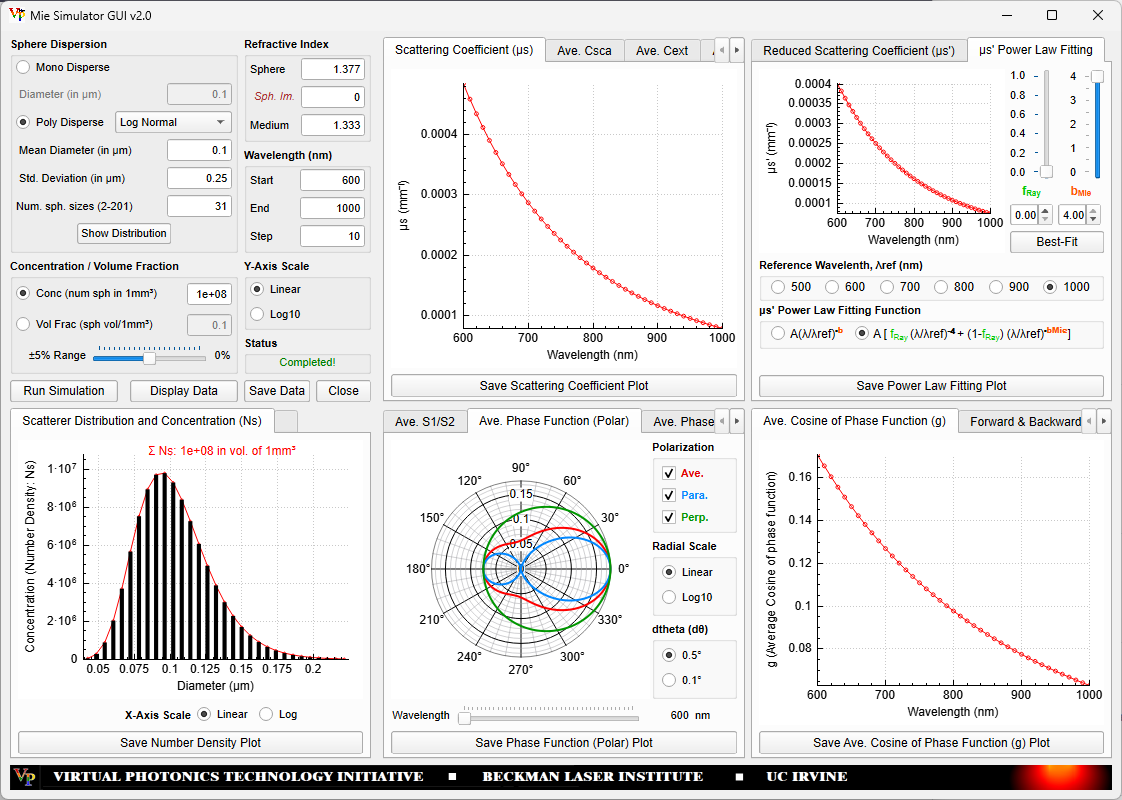
The Mie Simulator GUI is an open-source, user-friendly tool designed to calculate the characteristics of Mie scatterers.
This repository is a rudimentary c++ implementation of Mie scattering. It is meant to be used as a library for fast and stable low level evaluation of Mie scattering phenomenons.
|
|
 |
|