|
|
 |
SMUTHI
SMUTHI by Amos Egel solves 3D light scattering problems involving one or multiple particles (spheres, spheroids and finite cylinders) inside a planarly layered medium. It is based on the T-matrix method for the individual particles and on the scattering-matrix method for the propagation through the layered medium. For spheroids and finite cylinders, the particles' T-matrices are computed using the NFM-DS package by Adrian Doicu, Thomas Wriedt and Yuri Eremin.

PyTMatrix, by Jussi Leinonen, A Python code for computing the scattering properties of homogeneous nonspherical scatterers with the T-Matrix method.
A java app of Mackwoski and Mishchenko's Superposition T-matrix code for studying the light scattering properties of cosmic dust aggregates. The Java Superposition T-matrix App (JaSTA) software package consists of a Graphical User Interface (GUI) in the front hand and a database of related data’s in the back hand. JaSTA provides a unique and very much user friendly GUI that guides the user at each and every step. It is freely downloadble.
T matrix code for scattering by homogeneous particles with discrete symmetries by Michael Kahnert. For particle morphologies with geometric symmetries, the code makes use of group theory to systematically simplify the numerical solution to Maxwell's equations.

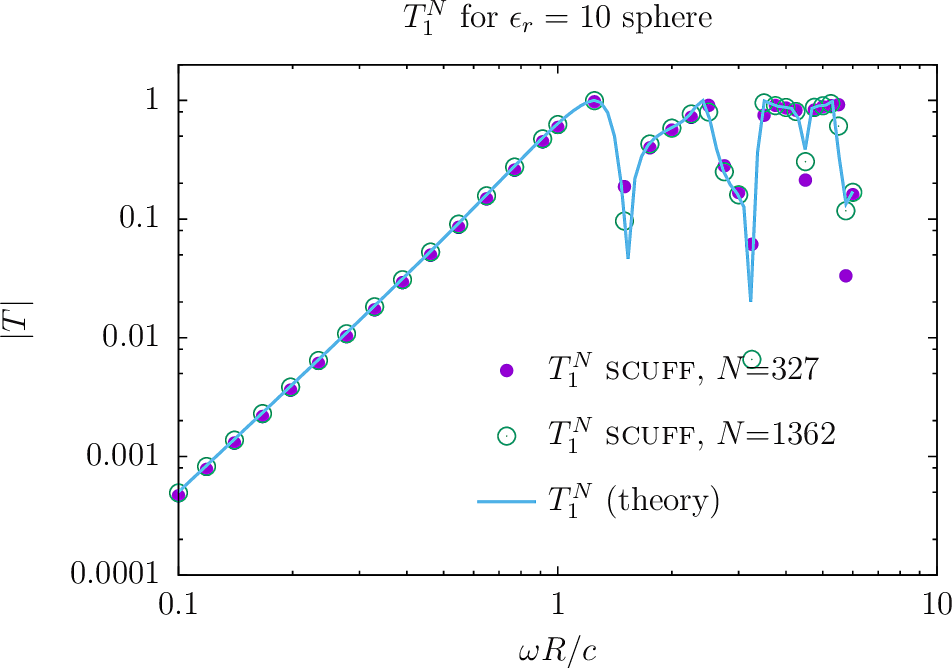
Computing T-Matrices of arbitrary objects by M T Homer Reid. This code is not restricted to rotationally symmetric scatteres.
- Link ( 5 Jul 2013, 31 Jul 2015) offline
- Link (10 May 2022)
Modification of the original Barber and Hill T-Matrix Fortran codes by Peter Alsholm. Using a larger T-matrix, more integration-points and extended prectston variables, converged solutions are possible for particles with larger size parameters and axial ratios. Code printed in
Light Scattering by Individual and Groups of Spheroidal Particles. diploma paper by Peter Alsholm, Lund Reports on Atomic Physics, LRAP-200, Lund, August 1996.
Fortran code for electromagnetic scattering from a lossy dielectric imbedded within another lossy dielectric (coated spheroid) and the Mueller matrix (averaged Stokes matrix) for a distribution of scatterers with a prescribed orientation distribution. Code by Larry Carey.
The Multiple Sphere T Matrix Fortran-90 Code by Dan Mackowski.
MSTM is a package for calculating the electromagnetic scattering and absorption properties of systems of spheres.
The code is designed to run on distributed memory parallel platforms, and uses MPI instructions in conjunction with fortran-90.
Initial release date: 15 January 2011.
Computational Electromagnetics Research Laboratory (CERL) has recently released a 3D-TLM simulator and its X-Windows based GUI front end.
Executable T-Matrix program 'Mieschka' developed under Linux to compute scattering by rotationally symmetric scatterers is available on CD-ROM with the book: Tom Rother: Electromagnetic Wave Scattering on Nonspherical Particles: Basic Methodology and Simulations. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York 2009.
|
|
 |
|

