|
|
 |
gprMax3D
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a non-destructive electromagnetic investigative tool used in many diverse applications across the fields of engineering and geophysics.
Mie Simulator GUI
This is a Mie Simulator GUI application. Mie Simulator GUI tool is capable of calculating
- Scattering coefficient
- Scattering cross section
- Reduced scattering coefficient
- Phase function
- S1 and S2
- Average cosine of the phase function
for a single or series of wavelengths
- Link (10 Aug 2015, offline)
- Link (6 Nov 2021)

VCRMEll2D
VCRMEll2D by Kuan Fang Renis the first realization of the Vectorial Complex Ray Model - VCRM developed by the author. By introducing the property of the Wavefront in the geometrical optics model, the VCRM can calculate very precisely the interaction of a wave of any form with a object of smooth surface and size much larger than the wavelength of the incident beam.
Virtual Tissue Simulator
Virtual Tissue Simulator (VTS) is a modular and scalable computational platform, to provide an integrated suite of computational tools to define, solve, visualize, and analyze relevant forward and inverse radiative transport problems in biomedical optics. This is a beta release of a MATLAB interoperability package that works with the Windows version of MATLAB.

Absphere
Abshere by Kuan Fang Ren is based on the rigorous theory to calculate various physical quantities in the interaction of a light beam with a homogeneous spherical particle or with a concentric layered refractive index gradient. ABSphere allows to calculate: (1) scattering diagrams, (2) radiation pressure (force) and torque exerted by a beam of light on the particle, (3). internal and external electromagnetic fields, (4). extinction, scattering and absorption sections. The forms of the beam considered in ABSphere: (1) circular Gaussian beam. (2) elliptical Gaussian beam. (3) Dungnut beam of 4 different polarizations, (4). Bessel beam (5).
- Link (31 Jul 2015, 23 Sept 2021)
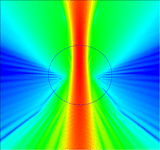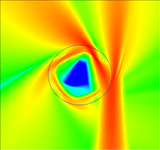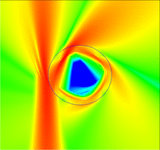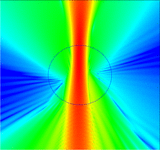
NPL Simulations
This code by Giuseppe Toscano is an extension to the COMSOL 4.2a RF Module. It is based on the hydrodynamic model which incorporates nonlocal effects in the optical response of nanoplasmonic structures. The extension can only handle 2D structures.

JFEM3D
JEM3D ist an FEM solver by Jeffrey M. McMahon which solves the vector wave equation for the electric or magnetic field directly.

MAXDGTD by Hassan Fahs is a discontinuous Galerkin code for solving Maxwell's equations in the time-domain (DGTD). It is a Fortran code.

ddscat-inputgen
ddscat-inputgen by Justin E Moore generates roughened spheres and spheroids geometries via Monte Carlo for DDSCAT simulation.

|
|
 |
|