|
|
 |
Superellipsoid Scattering Tool (Windows 98, 2000, XP) for T-matrix scattering computation by superellipsoids and other abritrary shaped 3D scatterers by T. Wriedt.
- SScaTT
Superellipsoid Scattering Tool (v.1.1.4) for T-matrix scattering computation by superellipsoids and other abritrary shaped 3D scatterers by T. Wriedt. Windows 98, XP SScaTT paper
- Particle shapes that might be suitable for SScaTT (Dec 2021)
- For questions please send emails to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (22.9.2006)
Fortran code for Electromagnetic Scattering by Spheroids by Peter G. Martin.
MMP FORTRAN code for electromagnetics simulation available on disk in
Christian Hafner, Lars Bomholt, The 3D Electromagnetic Wave Simulator, Wiley, Chichester 1993.
The book is out of print, but the tex-file and an executable code of 3D MMP compiled for Windows NT is available from Christian Hafner's server, ETH Zürich.
This code may be used for scattering by nonspherical nonsymmetrical arbitary 3D bodies. It has been applied to spheres in a Gaussian beam, spheroids, plates, cubes, finite cylinders, rain drops, spheres having multiple inclusions, clusters of spheres, spheroids and plates.
Please ask me for further information: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
- Link (27 Nov 2008, offline)
- Link (9 Dec 2021, Internet Archive)
laser: 532nm, d=4µm, fiber: 5µm*1.5µm, n=1.5

Classical Fortran 77 code based on a Separation of Variables Method scheme using spheroidal development, kindly made available by Shoji Asano, to compute scattering by spheroidal particles.
Published in:
Shoji Asano and Giichi Yamamoto: Light Scattering by a Spheroidal Particle.
Applied Optics, Vol. 14, Issue 1, pp. 29-49 (1975) .
The code, additional information by Shoji Asano and the corresponding paper can be found
- here (local copy on Bremen server) 3 Mar 2011
For scattering by 2D bodies e.g cylinder available on disk in
Christian Hafner, 2-D MMP: Two Dimensional Multiple Multipole Analysis Software and User´s Manual, Artech House, Boston 1990.
The book is out of print but book and code are available from Christian Hafner's server.
This code calculates the extinction, scattering and absorption efficiency factors for prolate or oblate homogeneous spheroids. The separation of variables method (SVM) and an original scheme of solution of the light scattering problem are used.
A demo version of this programme is available from the Wiley site and the MaX-1 ETHZ site.
This is a new 2-D version of the MMP technique with a wide range of application including statics, scattering, gratings, antennae, guided waves, resonators and discontinuities.
The full version is: Christian Hafner: MaX-1, A Visual Electromagnetics Platdform for PC's. CD-ROM and Getting Started with MaX-1 Guide. Wiley, Chichester, 1998.
- Link - MaX-1 MMP GMT (27 Nov 2008)
- Link - John Wiley & Sons (27 Nov 2008)
FORTRAN SP-PM (simple point matching) code by Politecnico di Milano for RADAR scattering by axisymmetric rain drops. Theory based on T. Oguchi (1973).
Available by FTP from ESA/ESTEC server.
ScattPy
ScattPy is an open source Python package for light scattering simulations. Its goal is to provide an easy-to-use and flexible modern framework for the numerical solving of the diffraction problems with various kinds of particles. ScattPy includes the separation of variables (SVM), extended boundary condition (EBCM) and point matching (PMM) methods.
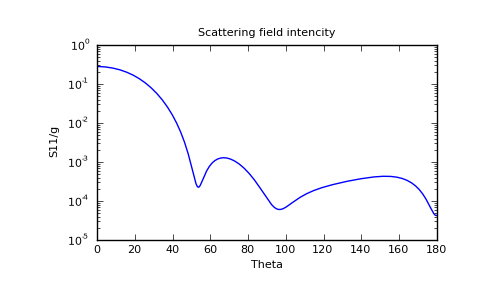
FORTRAN point matching code by ESA (European Space Agency) for RADAR scattering by axisymmetric rain drops. Theory based on J.A. Morrison, M.J.Cross (1974) and T. Oguchi (1973).
Available by FTP from ESA/ESTEC server.
|
|
 |
|